Class-12 formula Notes is a most important part for exploring the Knowledge about Science, Mathematics fundamental conspectus is clear with the help of this formula class 11 & 12 syllabi is divided on the different criteria suck as Physics, Chemistry, Mathematics this major subject is needed for various National & International Examination (Olympiad, fellowship program, University exam )admission based on three major syllabi Class-12.
PCM Formula is helpful for easily solved the problem is related to Asking in Question various topics such as important in physics, Electric charge& Field, Electrostatic potential and capacitance, Resistance, Current electricity, Moving charges and magnetism, Magnetism & matte, Electromagnetic induction Ray & optics, Wave Optics Atomic And Nucleus, Semiconductor, so many topics notes are here.
This topics Quiz is also Organized on the E-learningadda.com platform for increasing the knowledge & motives of all candidates to work in the science field And crack all examinations related to the Syllabi IITs, NITTS, KVPY, NTSE, and research Institute organized various examination also this syllabi is Medical Student is also used for memories the fundamental formula for helping solved many types of Question, below the section some major topics Question formula is here so many doubt is clear after ready all Fundamental based Question.
Physics Formula Details
 | |
 | |
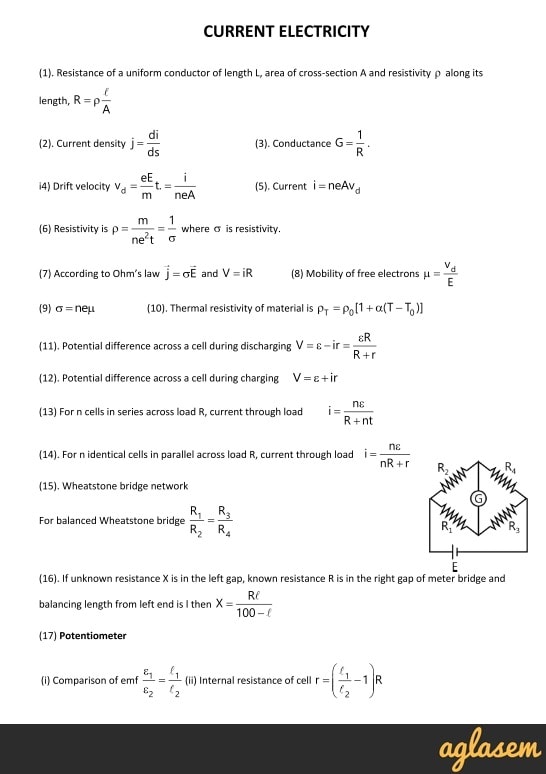 |  |
 |  |
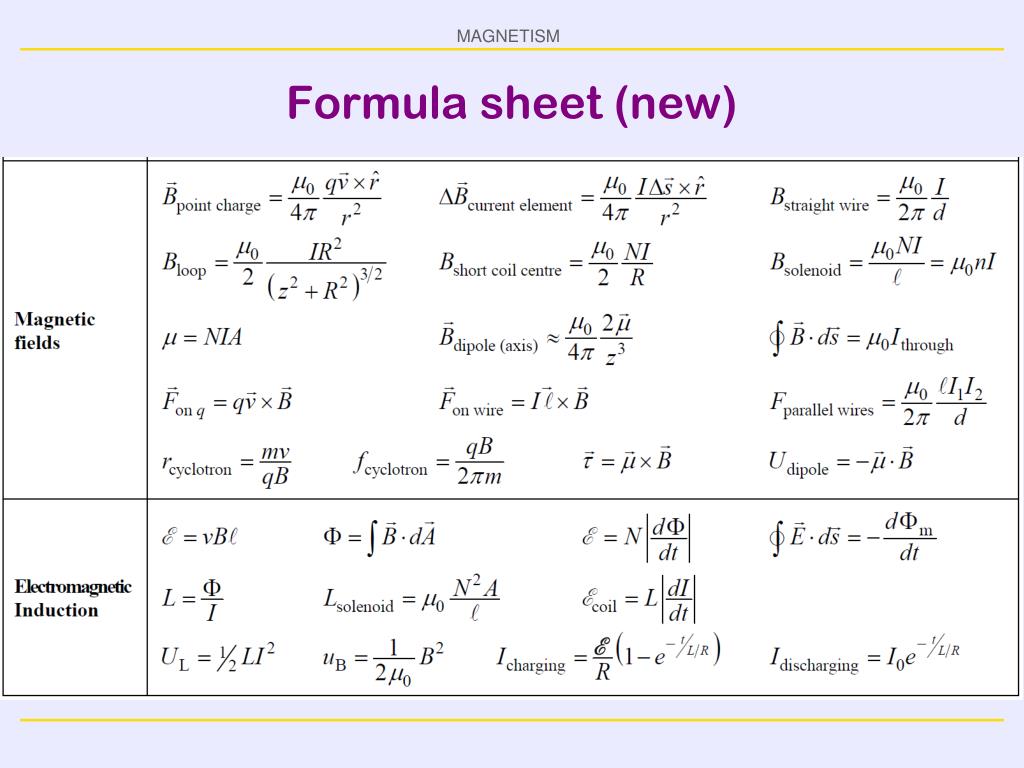 |  |
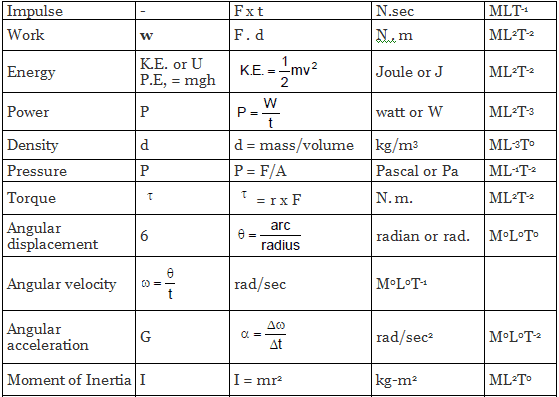 | |
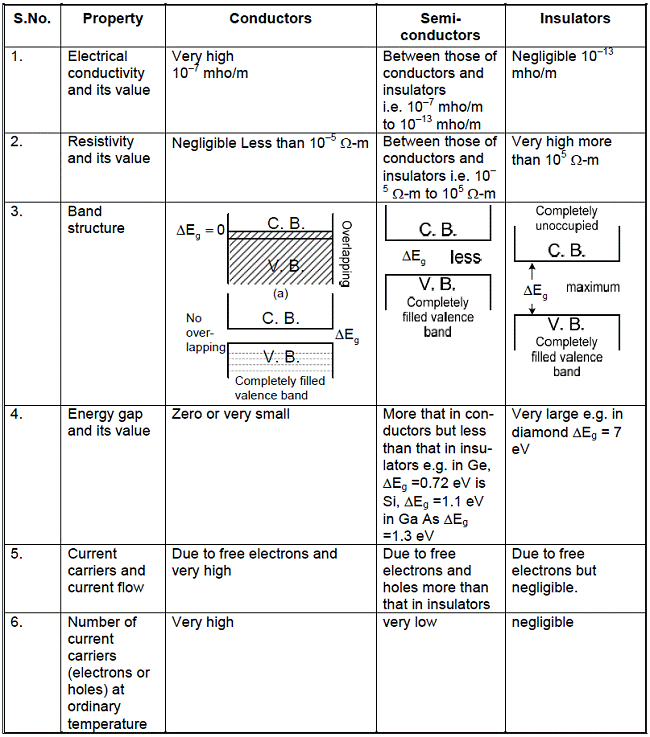 |  |
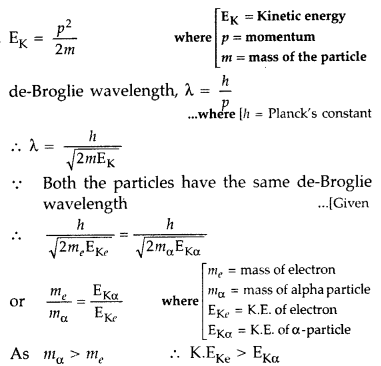 |  |
 |  |
Important Pdf In based Of fundamental Formula
| HCV_1-Concept-of-Physics.pdf | HCV_2-Concepts-of-Physics.pdf |
| Click here.pdf | Click here.pdf |
| Click here.pdf | Click here.pdf |
| Click here.pdf | Click here.pdf |
Chemistry Formula Details
Increasing or Decreasing Order
| Melting point=Li > Na > K > Rb > Cs | Colour of the flame= Li-Red, Na-Golden, K-Violet, Rb-Red, Cs-Blue, Ca-Brick red, Sr-Blood red, Ba-Apple green |
| Stability of hydrides = LiH > NaH > KH > RbH> CsH | Basic nature of hydroxides= LIOH < NaOH < KOH < RbOH < CsOH |
| Hydration energy= Li> Na > K> Rb > Cs | Reducing character= Li > Cs > Rb > K > Na |
| Stability of +3 oxidation state= B> Al > Ga > In > T1 | Stability of +1 oxidation state= Ga < In < TI |
| Basic nature of the oxides and hydroxides= B< Al< Ga < In < TI | Relative strength of Lewis acid= BF3 < BCl3 < BBr3 < BI3 |
| Ionisation energy= B> Al In SiO2 > Ge02 > SnO2 > PbO2 | Reducing nature of hydrides= CH4 < SiH4 < GeH4 < SnH4 < PbH4 |
| Thermal stability of tetrahalides= CCl4> SiCl4> GeCl4> SnCl4 > PbCl4 | Oxidising character of M+4 species= GeCl4 < SnCl4 < PbCl4 |
| Ease of hydrolysis of tetrahalides= SiCl4 < GeCl4 < SnCl4 < PbCI4 | Acidic strength of trioxides= N203 > P2O3 > As2O3 |
| Stability of trihalides of nitrogen= NF3 > NCl3 > NBr3 | Lewis base strength= NF3 PCI3 > AsCl3 > SbCl3 > BiCl3 |
| Melting and boiling point of hydrides= H2O > H2Te > H2Se >H2S | Volatility of hydrides= H2O < H2Te < H2Se < H2S |
| Bond energy of halogens= Cl2 > Br2 > F2 > I2 | Covalent character of hydrides= H2O < H2S < H2Se < H2Te |
| Solubility of halogen in water = F2 > Cl2 > Br2 > I2 | Oxidising power= F2 > Cl2 > Br2 > I2 |
| Enthalpy of hydration of X ion= F- > Cl- > Br- >I- | Reactivity of halogens:= F> Cl> Br > I |
| The ionic character of the M-X bond in halides = M-F > M-Cl > MBR > M-I | Reducing character of X ion:= I- > Br- > Cl- > F Acidic strength of halogen acids= HI > HBr > HCI > HF |
| Oxidising power of oxides of chlorine = Cl2O > ClO2 > Cl206 > Cl2O7 | Decreasing ionic size= 02- > F- > Na+ > Mg2+ Increasing acidic property= Na2O3 < MgO < ZnO< P205 |
| Increasing bond length= N2 <02 < F2 < CL2 | Increasing acid strength= HClO < HClO2 < HClO3 < HClO4 |
Topics wise formula
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
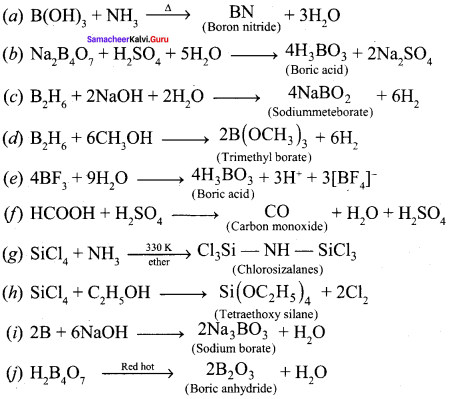 |  |
 |  |
Some fundamental Pdf for Revision
| Click here.pdf | click here.pdf |
| Click here.pdf | Click here.pdf |
| Click here.pdf ALCOHOL-PHENOL-ETHER-.pdf | Click here |
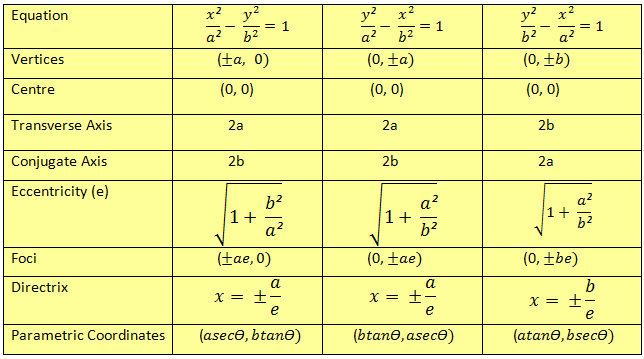
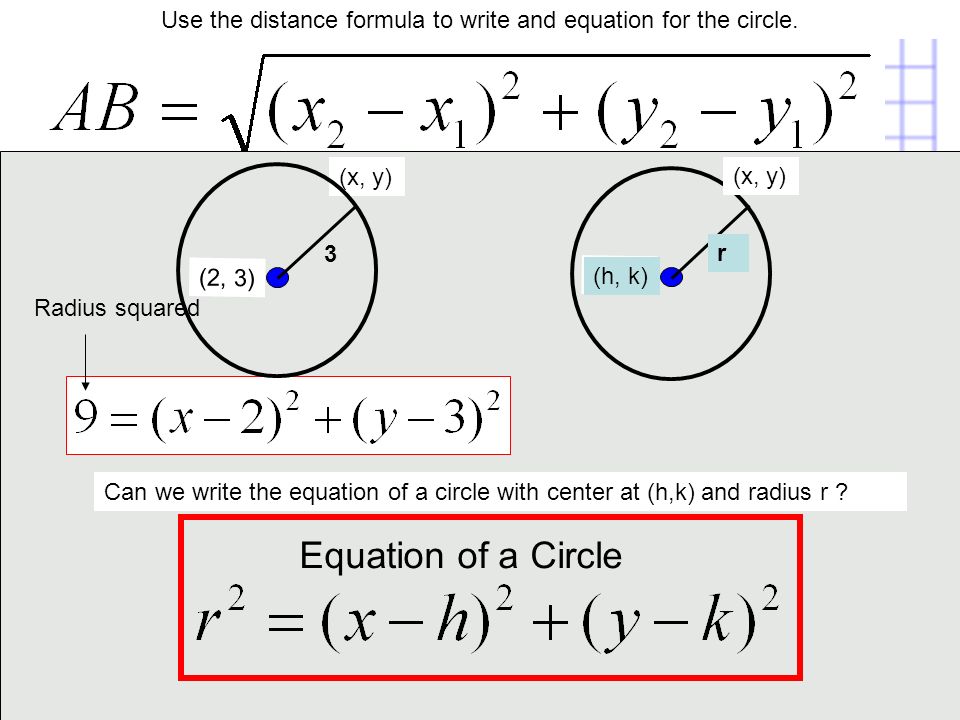
Mathematics Formula Details
 |  |
 |   |
 |  |
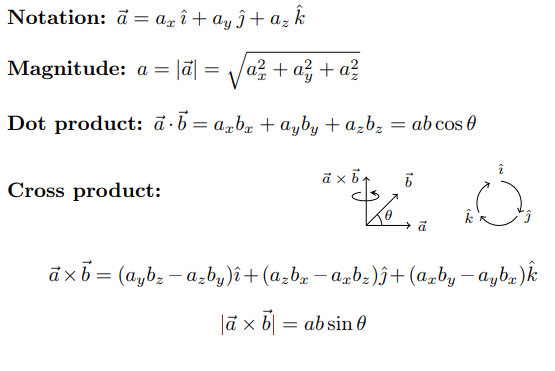 |  |
  |  |
 |  |
![Maths Top 50 Formulas - [PDF Document]](https://reader020.staticloud.net/reader020/html5/20190717/55c37abdbb61eb6b5e8b45a2/bg1.png) |  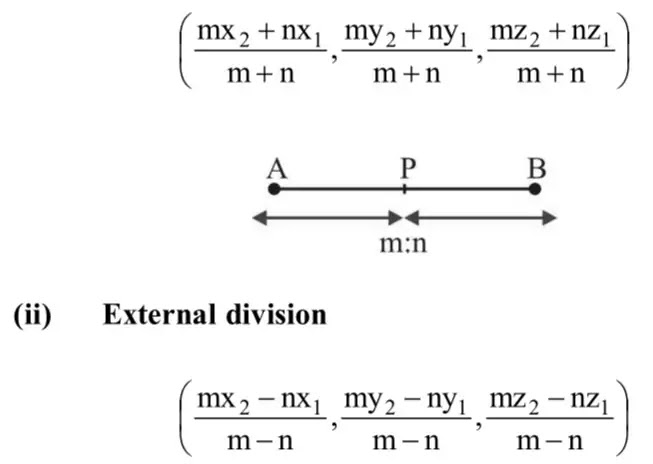 |
.gif) |  |
  |   |
 | |
 |  |
.gif)  |
Important Formula on Mathematics
| 1) sin θ = sina and cosθ = cosa ⇒ θ = 2nπ + a | 2) sin θ = 0 ⇒ θ = nπ |
| 3) cosθ = 0 ⇒ θ = (2n + 1)π/2 | 4) tan θ = 0 ⇒ θ = nπ |
| 5) sinθ = sina⇒ θ = nπ + (-1)na where a ∈ [–π/2, π/2] | 6) cosθ= cos a ⇒ θ = 2nπ ± a, where a ∈[0,π] |
| 7) tanθ = tana⇒ θ = nπ+ a, where a ∈[–π/2, π/ | 8) sinθ = 1 ⇒ θ= (4n + 1)π/2 |
| 8) sinθ = 1 ⇒ θ= (4n + 1)π/2 | 9) sin θ = -1 ⇒ θ = (4n – 1) π /2 |
| 10) sin θ = -1 ⇒ θ = (2n +1) π /2 | 11) |sinθ| = 1⇒ θ =2nπ |
| 12) cosθ = 1 ⇒ θ =(2n + 1) | 13) |cosθ| = 1⇒ θ =nπ |
| sin 3x = 3 sin x – 4 sin3x | cos3x = 4 cos3x – 3 cosx |
| tan 3x = (3 tan x – tan3x) / (1- 3tan 2x) | tan 2x = 2 tan x / (1-tan 2x) |
Revision Notes PDf
