IBPS-AFO-The Institute of Banking Personnel Selection (IBPS) Agricultural Field Officer (Scale I) mainly revolves around propagating bank’s financial products and services amongst the farmers and landlords in the rural areas for Agricultural purposes.
IBPS provides its services to all public-sector banks, SBI, RBI, NABARD, SIDBI, LIC & Insurance Companies, and other Banks which are regular members of the IBPS society.
Syllabus IBPS-AFO-Click here
Basic Notes in IBPS-AFO
- Definition: The word “agriculture” is derived from Latin words,” Ager /Agri “means “soil “and ‘culture “ means “’ cultivation “Agriculture is a practical science that includes all attributes of crop production and development involving agronomy Forestry, Horticulture, Fishing. Live-stock. etc.
- Agriculture is the Art and Science of cultivating the soil, growing crops, and raising livestock. It includes the preparation of Plant and animal products for people to use and their distribution to markets.
- Agriculture provides most of the world`s food and fabrics. Cotton, wool, and leather are all agricultural products.
These products, as well as the agricultural methods used, may vary from one part of the world to another.- Art: this includes knowing how to skillfully perform farm operations, But certainly doesn’t involve knowledge of the operative principal behind the farm management.
- Science: Use of all the available technologies developed according To scientific value such as plant breeding, production, protection,economical methods, etc. to increase crop yield and farm profit.
- Techniques e.g., new crop varieties production by crossbreeding of pest and disease resistant plat varieties, production of crop hybrids, varietieswith high sensitivity to fertilizers, water management, herbicides forweed control,
- The use of bio-control agent for pest and disease, etc. are all included in science.
- Techniques e.g., new crop varieties production by crossbreeding of pest and disease resistant plat varieties, production of crop hybrids, varietieswith high sensitivity to fertilizers, water management, herbicides forweed control,
- Business:- As long as agriculture is a rural lifestyle, food production is eventually linked to consumption. However, as a business.
- It seeks to maximize its bottom line by managing agriculture labor, capital, and Water using the information to produce food, fiber, and fuel.. Recently.
- Agriculture has transformed into a commercial to be adapted as a business through modern automation.
- Agriculture includes several fields like horticulture, seed growing, dairy farming and animal husbandry, use of land as pastures, grasslands, vegetable gardens, and forest nurseries, and the use of land for forests where they are used for agriculture purposes and use of land for agricultural purposes.
Evolution of Agriculture and Role of Humans
Agriculture has passed through several states during the process of agriculture development and human civilization. Humans have played a
significant role in agriculture development by engaging them in hunting, cattle breeding, crop cultivation, and trade.
Hunting: It used to be the main food source. This is an important occupation and has been around for a very long time.
Pastoral: People received food from domestic animals, such as dogs, buffalo, horses, cows, etc. While living on the edge of the forests, to
feed the animals, humans kept migrating from place to place in search of food.
Crop Culture: Living by the riverbeds, humans obtained enough water for their animals and domestic plants and began to grow them. This led
them to settle in one place building communities.
Trade: when humans began to produce more than their needs, they started exchanging the surplus for other useful products, from there
the trading started. With agriculture development, infrastructure such as roads, routes, etc. also started developing. Agriculture became
civilized, starting with a trading culture.
- Branches of Agriculture
- There are 20 major branches of Agriculture:
- Agronomy
- Horticulture
- Plant Breeding and Genetics
- Seed Science
- Crop-Physiology
- Plant Pathology
- Plant Protection
- Soil Science
- Entomology
- Agriculture Biotechnology
- Agriculture Engineering
- Agriculture Economics
- Forestry
- Animal Husbandry
- Environmental Science
- Food Science and Technology
- Land and Water Management
- Agriculture Chemistry
- Agriculture Microbiology
- Home Science
As we have known that agriculture is a vast field and has several branches and sub-branches. A detailed explanation of fields of agriculture is given
below:
Agronomy: Branch of agriculture deals with the cultivation of crops, forage, food, fiber, oilseeds, sugar, etc. The primary aim of this branch is to improve food production and cropping techniques. It is the most important branch among all branches of agriculture. It covers vast types
of agriculture practices like permaculture, aquaponics, and playhouse, farming, etc.

Branches of Agronomy
There are 2 branches of Agronomy
1.Weed Sciences: Study of vegetation growth and management in agriculture fields, natural zones, and urban and residential areas.
- Organic Farming: A method of growing plants and animals naturally is known as farming. This involves biological materials, and averting the
use of synthetic substances, to sustain soil fertility ecological stability,minimalizing waste and environmental pollution. Moreover, the growing of micro greens also comes under organic farming.
Horticulture
Branch of agriculture deals with the plant’s cultivation that is directly used by humans for food, medicine, and aesthetic purposing.
Branches of Horticulture
There are 7 branches of Horticulture:–
- Pomology: Branch dealing with fruit culture is known as pomology.
- Floriculture: Branch of horticulture dealing with a vegetable cultivation such as beans, tomatoes, etc.
- Floriculture: The ranch of horticulture deals with flower cropping such as roses carnation, etc., and gardening.
4. Arboriculture: Branch of horticulture deals with the assortment, planting, maintenance, and removal of trees shrubs, and other woody plants.
5.Landscaping: Branch of horticulture dealing with the production, presentation, and care of landscapes, flowers, and other plants.
6.Viticulture: Cultivation and retailing grapes are known as viticulture.
7. Oenology: Study of all the characteristics of wine plants and wine-making.
Plant Breeding and Genetics:-
Branch of agriculture defines as the art and science of modifying the genetic structure and plants traits to obtain the desired character.
Seed Science
The branch deals with the seed structure and growth habitats starting from fertilization, egg development, and growing into a
new plant. Seed science is closely related to biochemistry, botany, genetic, and other bioscience.

Crop-Physiology
Crop Physiology is the study of the function and responses of plants grown in different environments. It is one of the most basic fields of agriculture.
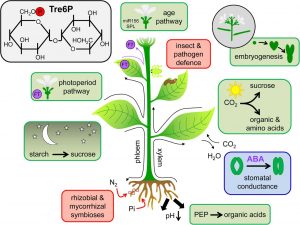
Plant Pathology
Plant Pathology deals with the causes of disasters, instabilities in plants, and the treatment of plant disasters.

Soil Science:-
Among Several branches of agriculture, soil science is of great significance because of its direct influence on plant growth and nutrient supply. The study of soil as a natural body that is creates by natural forces on the surface of the earth on which plants grow. The study of soil properties in relation to soil use and management, soil classification, formation, and mapping of the chemicals, physical, biological, and fertility properties, are known as soil science.
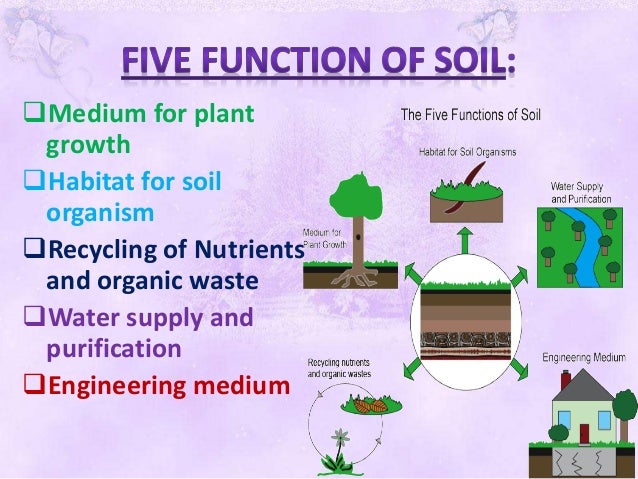
Branches of Soil Science
Among other branches of agriculture, soil science is the most important because it is the primary source of nutrition for the
plants.
There are 10 branches of soil science.
- Soil Chemistry: Study of the chemistry compositions, properties, soil process.
- Soil Biology: It concerns organisms living on the earth, their biology, function, and activity e.g. nematodes and insects.
- Soil Mineralogy: Branch focuses on primary and secondary soil-minerals and soil contribution, to develop physical and chemical structure of the soil. It also focuses on soil fertility and biology.
- Soil Genesis and Classification (Penology): Soil formation is associated with rocks and minerals weathering, as well as with aspects and courses of soil formation. Soil classification is a division of soil into group based on their properties.
- Soil Physics: The mechanical of the mass of the soil especially with water and soil energy.
- Soil Fertility: It is about the capability of the soil to deliver plants with the essential nutrients for their growth and development.
- Soil Salinity: Study of the excess of soluble-salts contained in the soil, their extraction, and soil treatment for agriculture.
- Soil Survey: Soil science involve the systematic inspection of soils on-site and in the laboratory, their classification, interpretation, and mapping.
- Soil Conservation: It is concerned with protecting the soil from physical destruction as a result of erosion (from water and wind) or chemical destruction. Thus, Soil protection is associated with a mixture of all management and land-use approaches that protect the soil from destruction due to natural or anthropogenic factors.
10.Soil Microbiology: while dealing with several fields of agriculture, soil microbiology examines soil for microbial communities. It deals with their role and characteristics in soil fertility and land reclamation, and particular plant nutrition through rooting or diseases caused by
phytopathogenic microbes in the soil.
Entomology
Branch of agriculture that studies insects and pests that are important to agriculture.

Branches of Entomology
There are 13 branches of entomology:
- Insect Ecology: The study of the relationship between insects and their environment. This section is devoted to the study and analysis of the ecosystem for the existence of the insects. The goal is to protect insects from being removed or exterminated.
- Insect Morphology: In this area of entomology, the body parts of insects and their functions are studied.. This branch is mainly associated with the outer parts of the insect’s body.
- Insect Pathology: These areas of entomology studies diseases and pathogens that can harm affect the well-being of insects. To save beneficial insects, the scientist use pathogens or vectors to get free of certain harmful insect pests.
- Insect Physiology: This deals with the body function and behavior systems of an insect. This includes studying the various behaviors of insects in relation to the ecosystem.
5. Insect Toxicology: The study of how insecticides and other chemicals affect the physiological functions of insects.
- Insect Taxonomy: Insect taxonomy is a practice of insect naming. This is an ongoing process as several un-identified insects are still roaming planet earth.
- Industrial Entomology: The Entomology branch deals with the cultivation of insects for commercial or economic purposes. These include honey bees, bumble bees, butter flies, silkworms, etc. This branch is concerned with the benefits of humanity. On the other way, this also applies to the removal of harmful from houses such as malaria, dengue, etc.
8. Medical and Veterinary Entomology: Insects harm not human beings but also animals. It covers all aspects related to veterinary health and medicine such as malaria, dengue, etc.
- Biological Control Entomology: Insects harm not insects against harm-full insects. Use of friendly insect to take care of harmful insects know as biological control, e.g., wheat aphid ate by ladybird.
- Post-Harvest Entomology: Branch concerned with the study and insect control that harm stored food such as rice, wheat, etc.
- Forest Entomology: Study of the effects of insects’ on the forest and forest-products and development of a solution to protect forest trees from extreme damages.
- Forensic Entomology: Branch deals with the study of insects for legal purposes focus on the use of insect to clarify the place and time of human-health.
- Crop Protection Entomology: Studies ways to controls insects before harming the field crops are known as crop-production entomology, also “agriculture entomology”.
Agriculture Biotechnology
Branches of agriculture include the application of scientific techniques and tools, involving vaccines, molecular markers, genetic engineering, and tissue culture, to alter the genome of living organisms to develop improved organisms e.g. crops and livestock. In relation to several other fields of agriculture, currently, agricultural biotechnology is of major focus because of its genetic approach. Researchers believe that transgenic crops and animals could be a source to maintain a suitable food supply and fulfill global needs.
Agriculture Engineering
Works with agriculture machinery for preparation, sowing, harvesting, and post-harvesting operations, counting water and soil protection technologies and bioenergy.
Branches of Agriculture Engineering
- Agriculture Mechanization: The use of agriculture machinery to automate agriculture work, which significant increase the productivity of agricultural workers and production efficiency, mechanization promotes large-scale production.
- Farm Power and Machinery: Branch of agriculture in which the utilization and care of agricultural tools, machines and structures are done.
- Farm Structure: A building on a farm is used for agriculture purposes. Especially large-scale farms, used to accommodate farmer and their families or farm workers. Some of them can be utilized for growing crops, rearing live-stock, etc.
Agricultural Economics
An applied economic field that studies human behavior with respect to the relationship between food and fiber production and distribution.

Branches of Agriculture Economics
There are 7 fields of agriculture economics:
- Agrarian system: Economic and technical factors affecting agronomic practices.
- Agribusiness: Several businesses include agriculture product processing and farming, supply of seed, agrochemicals, equipment, marketing, and retail, etc. are all included in agribusiness.
- Agricultural Extension: Formerly known as the implementation of the latest research and knowledge to agriculture practice through farmer trainings. The expansion area now includes a wider ranges of communications and training activates planned by professionals in various field for the rural population, including agriculture, marketing, health care, and business management.
- Agriculture Marketing: Covers several related to the movement of agriculture products from farm to consumers, direct or indirect transfers.
- Custom Harvesting: The business of collecting plants for others. Harvesting is done with other people’s harvesting every year instead of buying their own. Custom harvesting usually have their own harvestings, and they work on the same farms every harvest season. Thanks to custom harvesting, farmers do not need to invest in expensive equipment while making the most of the machinery’s use for a low cost.
- Economic Development: Sustained concentrated action by politicians and communities to imp[rove living standards and economic health.
- Rural community Development: A set of approaches and activities aimed at improving the well-being and life of people living in rural areas. Improving rural activities will sustain population stability by lowering rural urban migration.
Forestry
Forestry is engaged in the extensive cultivation/farming of perennial plants for the supply of rubber, timber, etc. as well as industrial raw-material.

Branches of Forestry
There are 6 branches of forestry:
- Agro-Forestry: Agroforestry is a science that deals with land-use management system for growing trees, shrubs, on or between crops.
- Rangeland Management: Natural science focuses on the study of pastures and “the maintenance and sustainable supervision of dry
lands for the benefit of today’s society and future generations. - Wildlife Management: Studies to be balance the wildlife with those needs of humans using the latest scientific evidence.
- Analogy Forestry: A system of planned managed forests that are primarily used in tropical or sub- tropical zones.
- Forest Gardening: A low maintenance plant-based food agro-forestry system grounded on forest eco-systems with fruits and nuts
trees, shrub, grasses, vine, and perennial vegetables that benefit directly from the yield. - Forest Farming: Agro- forestry practices are categorized by 4I’s –International, Intensive, Integrated, and Interactive supervision of a
prevailing Forest ecosystem in which forest-health is supreme.
Animal Husbandry

Branches of Animal Husbandry
There are 9 branches of animal husbandry:
- Dairy Farming: Human demand for milk is met by the dairy sector, which means the long accessibility and production of milk, which is then treated to ultimately meet society’s milk need.
- Sericulture: A branch of agriculture that cultivates silk, which grows silkworms for silk production and commercial purpose, especially the Bombyx mori L. species.
- Aquaculture (Fishery): Branch engaged in fish farming and rearing, counting marine and in-land fish to provide food and manure.
- Mari culture: A specialized aquaculture industry that includes the rearing of the marine organism for food and added products in the ocean, in closed, or in reservoirs filled with sea water.
- Nematology: An essential branch that studies a noble diverse group of round worms known as nematodes, which are found in virtually all environments around the world.
- Apiculture or Beekeeping: Beekeeping means raising and keeping colonies of honey bees, usually in artificial and natural hives, to
obtain honey from bees and other bee goods. - Poultry: Poultry farming also one of the branches that deals with birds that are bred to meet the food requirements for eggs, meat
feathers. - Nomadic Pastoralism: Rearing of livestock during the phase of migration from region to region in pasture and clean water
search. - Piggery: Concerned with the rearing and breeding of pigs for the live-stock needs.
Environmental Science
The field that mixes biological, physical, and informational science in the study of the environment and solving ecological problems.

Branches of Environmental science
There are 2 branches of environmental Science:
- Energy & Environment: Branch deal with the potential of bio-energy as an economical engine for rural growth and a growing
awareness of worldwide climate change. - Agro-Meteorology: Agro-meteorology deal with studies of the environment’s physical conditions for the cultivation of plants
or animals.
Food Science and Technology
Among known fields of agriculture, food science, and technology uses a variety of approaches to study the composition of food, processing, packaging, and selection of existing foods products.
- Food and Nutrition: corporal and economical access to decent and cheap nutritious food is a primary function of the agriculture sector by supporting an increase in production, improving storage and postharvest handling,, and reducing transportation costs.
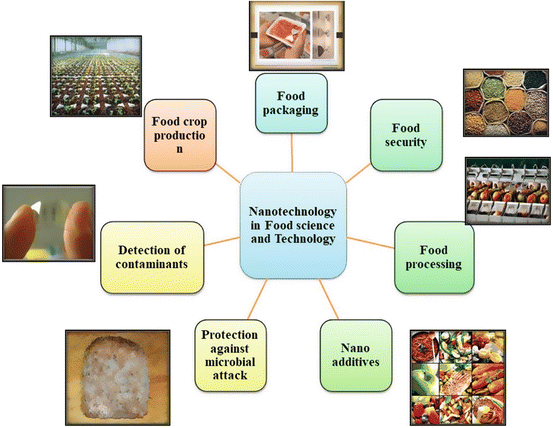
Land and Water Management:-
The process of management and expansion of land resources. Resources are mainly used for organic farming, water management, reforestation, and ecotourism projects.
Branches of Land and Water Management
There are 2 branches of land and water management
- Soil and water conservation: This branch deal with reducing runoff through structure or land-use to reduce erosion.
- Irrigation & Drainage: Irrigation and drainage, artificial land irrigation or artificial excess-water removal from the land. As some areas need to be irrigated or drained already so can be used for agriculture.
Agricultural Chemistry
Among branches of agriculture, this specific branch deals with chemistry, particularly organic and bio-chemistry, related to agriculture, production, and raw food processing into desired foods and drinks, and environmental restoration.

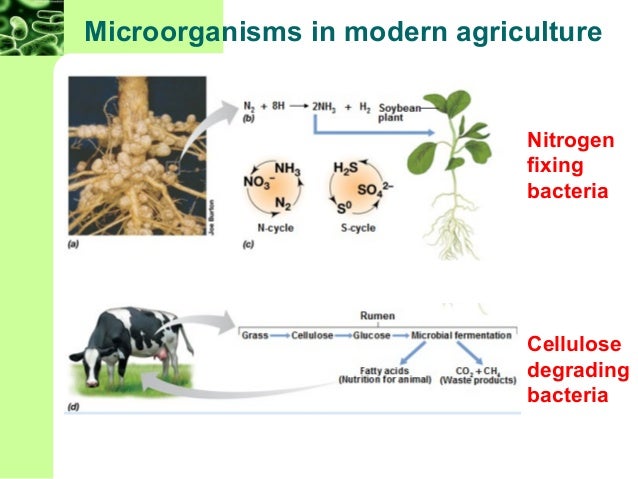
Agricultural Microbiology
Branch of agriculture deals with the part micro-biology that deals with microbes linked with diseases of plants and animals. Deal with the study of soil fertility restoring micro-biology e.g., microbial decomposition of organic matters and the conversion of nutrients in the soil.
Home Science
A most interesting branch of agriculture deals with the best application and use of agriculture products in healthier means.
Seed Multiplication Ratio
| Paddy | 1:80 |
| Hybrids | 1:100 |
| Wheat | 1:20 |
| Maize | 1:80 |
| Lowest For Potato | 1:4 |
| Groundnut | 1:8 |
Minimum Seed Germination % Required
| Rice | 80% |
| Wheat | 85% |
| Maize | 90% |
| Groundnut, Soybean, Sunflower, Caster (All Oil Seeds ) | 70% |
| Sorghum, Pearl Millet, Mung | 75% |
| Cotton Lint | 65% |
| Cotton, Declined | 70% |
| Tomato | 70% |
| Onion, Cabbage, Brinjal | 70% |
| Okra, Cauliflower | 65% |
| Capsicum, Chili, Carrot, Sugar Beet | 60% |
Important Notes
| 1. Science Of Rearing Honey Bees Is Called Apiculture. |
| 2.Queen Fertile Female- Responsible For Laying Eggs. |
| 3.Works strike Female- Born From Fertilized Eggs. |
| 4.Drone Male Insect – Male Bees Unfertilized Eggs |
| 5. Foraging Means Collection Of Pollen And Nectar By Honey Bees |
| 6. Queen Bee Emits Pheromones That Can Encourage Male Drones To Mate |
| 7. Nuptial Flight Is Also Known As Marriage Flight Of Honey Bees |
| 8. Swarming It Is A Behavior In Honey Bees Which Encourages The Bees To Come out of The Hive In Large Numbers To Relieve From Overcrowding In The Colony |
| 9. Absconding Means When The Entire Colony Leaves Off The Place And Establish The Colony At Another Suitable Place. |
| 10. Royal Jelly Is Produce In Hypopharyngeal Glands Which Is Produced By Nurse Bees At The Age Of One Or Two Weeks And It Is Queen Larvae And Young Workers. |
Important MCQ Question
The answer is shared in the comment section
1) Based on covering material which among the following are the types of the greenhouse.
A. Glass glazing
B. Even spa
C. Wooden framed
D. Cooling fan pad type
E. None of these
2) What is the premium rate for Kharif under PMFBY:
A. 1.5%
B. 2.5%
C. 5 %
D. 2 %
E. None of these
3) Which among the following propagation method is used in Viney:
A. Mound layering
B. Trench layering
C. Serpentine layering
D. Tip layering
E. Air layering
4) In which type of tillage system is 15 -30 % plant residue left on the soil surface:
A. Reduced tillage
B. No-till
C. Conventional tillage
D. Ridge tillage
E. Mulch tillage
5) Which nutrient deficiency symptoms are major veins remain green, top vein become short and slender, and chlorosis on new leaves:
A. Fe
B. Mn
C. Cu
D. Ca
E. None of these
6) Sponge-like appearance in mango is due to:
A. Downey mildew
B. Powdery mildew
C. Tip necrosis
D. Sponge tissue
E. None of these
7) The uniform Premium rate for Oilseed crops under PMFBY is:
A. 1.5 %
B. 2 %
C. 2.5 %
D. 3 %
E. None of these
8) E – NAM was launched in which years:
A. 2014
B. 2015
C. 2016
D. 2017
E. 2018
9.) What is the Field capacity of tractor drawer harrow:
A. 0.5 ha /day
B. 0.75 ha /day
C. 1.0 ha /day
D. 1.5 ha /day
E. None of these
10) According to NHM, the Lowest production of which commodities in 2017—18.
A. Vegetable
B. Fruits
C. Plantation crop
D. Medicinal crops
E. None of these
11.According to NHM, the highest production of which commodities in 2017-18:
A. Vegetables
B. Fruits
C. Plantation crop
D. Medicinal crops
E. None of these
12. What is the unit cost/ha for reclamation of acidic soil, under RKVY :
A. 10000 / ha
B. 15000 /ha
C. 30000 / ha
D. 60000 / ha
E. None of these
13. Which among the following crop is the low to medium sensitive to water shortage:
A. Wheat
B. Cotton
C. Millet
D. Sorghum
E. None of these
14) Which among the following crop is the low sensitivity to water shortage:
A.Wheat
B.Cotton
C.Millet
D. Sorghum
E. None of these
15) MSP of Common Paddy in 2018 -19?
A.1750
B. 1775
C. 1850
D1875
E. None of these
16) The highest exporting destination for Banana is:
A. Saudi Arab
B. Qatar
C. Oman
D. Kuwait
E. None of these
17. What is the capacity of high volume spray:
A. Less than 5 l /h
B. 50 – 75 l/ha
C. 100- 200 l/ha
D. 150 – 250 l/ha
E. More than 400 l/ha
18. Which of the following organism does not supply nitrogen:
A. Azotobacter
B. Rhizobium
C. Trichoderma Miridae
D. All of these
E. None of these
19. According to RBI guidelines maximum limit of loan for SC/ST under the weaker section is:
A. 1 lakh
B. 50000
C. 1.5 lakh
D. 2lakh
E. None of these
20. PMFBY launched in which year:
A. 2014
B. 2015
C. 2016
D. 2017
E. 2018
21. pH value of acidic soil is:
A. Less than 7
B. 8.0
C. 8.5
D. Both B & C
E. More than 8.5
22. Nitrogen percentage in CAN:
A. 15 %
B. 20 %
C. 25 %
D. 33 %
E. None of these
23. A number of markets covered under E- NAM till March 2018:
A. 300
B. 350
C. 450
D. 500 -600
E. None of these
24. What is the capacity of medium-sized godowns is:
A. 50 MT
B. 200 MT
C. 250 MT
D. 1000 MT
E. More than 2000 MT
25. Which among the following has the lowest seed replacement rate:
A. Wheat
B. Paddy
C. Pigeon pea
D. Groundnut
E. Black gram
26. What is the premium rate for Rabi crops under PMFBY:
A. 1 .5 %
B. 2 %
C. 3 %
D. 2.5 %
E. 5 %
27. What is the maximum limit of loans for building social infrastructure as per RBI?
A. 50 lakh
B. 75 lakh
C. 2 crore
D. 5 crore
E. None of these
28. What is the pattern of assistance of below 20 HP drawn moldboard plows benefits other than SC /ST Women / Small and Marginal farmers?
A. 30 %
B. 35 %
C. 40 %
D. 50 %
E. None of these
29. What is the pattern of assistance of 20 HP tractors for SC/ST Women /small and Marginal farmers?
A. 30 %
B. 35 %
C. 40 %
D. 45%
E. None of these
30. What is the maximum Financial assistance for power tiller 8 BHP for women farmers?
A. 30 %, 35000
B. 35 %, 50000
C. 40%, 40000
D. 45%, 65000
E. None of these
31. The highest area of alkali soil is in which state?
A. Maharashtra
B. Uttar Pradesh
C. Madhya Pradesh
D. Himachal Pradesh
E. None of these
32. Daily Agriculture Wages (Man) for an operation like sowing, harvesting is lowest in?
A. Chhattisgarh
B. Maharashtra
C. Punjab
D. Haryana
E. None of these
33. Daily agriculture wages (Man) for operations like sowing, harvesting is highest in:
A. Haryana
B. Uttar Pradesh
C. Rajasthan
D. Delhi
E. Kerala
34. Guidelines was revised for Nari Shakti Puruskar in which year:
A. 2014
B. 2015
C. 2016
D. 2017
E. None of these
Seed Technology one-liner
- During seed germination , seed coat ruptures due to
Answer:- Massive glycolysis in endosperm and cotyledons - Seed develop from
Answer: -Ovule - An aluminous seed showing hypogeal germination is
Answer:- Maize - Proteinaceous past of maize endosperm is
Answer:- Aleurone layer - Vivipary is
Answer:- Seed germination inside the fruit the fruit while attached to the plant - A gas required for germination of pea seed is
Answer:- Oxygen - seed dormancy allows the plants to
Answer:- Overcome unfavourable climate conditions - Among the following which compound can induce seed dormancy
Answer:- ABA - Protective covering radical during seed germination is
Answer:- Coleorhiza - Germination is epigeal in
Answer:- Helianthus - Seed Viability is tested by the use of
Answer:– Chloride - Caryopsis is the seed of
Answer:- Wheat - TZ test is done to determine in
Answer:- Viability of seed - 14 Real value of seed is determined by percentage of Purity ,
Answer:- germination and market value - Real value of seed is
Answer:- Purity % x germination % /100 - The complete chemical name of dye used in seed viability test is.
Answer:- 2,3,5, tri –phenyl tetrazolium chloride - The progeny of breeder seed in called
Answer:- Foundation seed - Seed plot technique of potato is use to produce
Answer:-Virus free seeds - Seed rate of hybrid maize is
Answer:- 20 – 25 Kg / hec - 20 The seed rate for sarson main crop iss about
Answer:– 4 – 6 kg // hec - Foundation seed is produced from
Answer:- Breeder seed - Seed rate of tobacco in kg /hec
Answer:- 1 -1.5 kg / hec - In castor bean the aril which is associated with Micropyle is
Answer:- Caruncle - Seed replacement rate for hybrid is
Answer:- 100 % - Non – endospermous seed store their food reserves
Answer:– Cotyledons
Horticultural One-liner
| Question | Answer |
| 1. Latest hybrid mango variety from Maharashtra is | Malika |
| 2. Lawn in Mughal garden are | Terrace |
| 3.Litchi was introduced to India from | Japan |
| 4. Madonna lily is | Lilium conidium |
| 5.Mango malformation disease is caused By ………………….. deficiency | Bo |
| 6.Marigold is native of | Mexico South America |
| 7. Marmalade is prepared by | Citrus |
| 8. Marmalade must have | 1.0 % pectin |
| 9. Maturity time of muskmelon in north India is | February – March |
| 10. Maximum number of fruit plants can be planted in the orchard by the system | Hexagonal System |
| 11. Most popular method of propagation of mango is | Veneer grafting |
| 12. Most economic methods of irrigation orchard underwater system condition is | Drip irrigation |
| 13. Mucilage in cut flowers is responsible for | Blackening of vessels |
| 14. Mucilage style of gardening was developed by | Babar |
| 15. Multistorey cropping system is practiced in | Karnataka and Kerala |
| 16. Muscat red is a variety of | Pomegranate |
| 17. Name a fruit pant which bears fruit only once in its lifetime | Banana |
| 18. Name of the annual climber is | Lathyrus odoratus |
| 19. Name the fruit which is used as a hedge | Karonda |
| 20. On a weight basis ……..Kg of cutting of sweet potato are required per hectare of planting | 600 |
| 21. One gram of carrot contains about…….seed | 850 |
| 22. One gram of celery seed holds about…..seed | 2470 |
| 23. One gram of onions as estimated generally contains …….seed | 240 |
| 24. One gram of turnip seed holds……… seed | 460-500 |
| 25. Onion is propagated by | Seeds |
The scientific name of Horticultural Crops
| Sr.No | Crops | The scientific name of the crop |
| 1. | Mango | Mangifera indica L |
| 2. | Guava | Psidium gujava L. |
| 3. | Pomegranate | Punica granatum L. |
| 4. | Jack | Artocarpus heterophyllus |
| 5. | Jamun | Eugenia jambolana |
| 6 | Tomato | Lycopersicon esculentum Mill |
| 7. | Bhendi | Abelmoschus esculentus L. Moench. |
The scientific name of the crop
| Sr.No | Crop | The scientific name of the crop | |
| 1. | Onion | Allium cepa var. aggregatum L. | |
| 2. | Cluster beans | Cyamopsis tetragonolobus L. | |
| 3. | Pumpkin | Cucurbita moschata Poir. | |
| 4. | Ribbed gourd | Luffa acutangula Roxb. | |
| 5. | Bitter gourd | Momordica charantia L. | |
| 6. | Snake gourd | Trichosanthes anguina L. | |
| 7. | Ash gourd | Benincasa hispida Cogn. | |
| 8. | Bottle gourd | Lagenaria siceraria Standl. | |
| 9. | Cucumber | Cucumis sativus L. | |
| 10. | Cowpea | Vigna sinensis L.Walp. | |
| 11. | Lablab | Lablab purpureus var.typicus L. | |
| 12. | Potato | Solanum tuberosum L. | |
| 13. | Sweet potato | Ipomoea batatas L.Lam. | |
| 14. | Tapioca | Manihot esculenta Crantz. | |
| 15. | Elephant yam | Amorphophallus campanulate Blume. | |
| 16. | Colocasia | Colocasia esculenta L.Scott |








