Class-6 to 8 formula Notes (Science & Mathematics ) combo is here, this section is helpful for clear conspectus related to subject all NECRT Notes is combined in PdF format some Topic is valance electron, chemical formula, average speed, an important symbol, definition energy, watt, pressure temperature, chemical formula, important chapter pDf is also provide, the chemical reaction solution, the periodic table is based on atomic weight, force related definition also available, this fundamental concept is related on the high-level study is helpful. Notes PDF –Click here.pdf
Science Formula
Fundamental symbol Details
| Temperature | Kelvin (K) |
| Length | Meter (m) |
| Mass | Kg |
| Weight | Newton |
| Volume | Cubic Meter |
| Density | Kg/ meter3 |
| Pressure | Pascale (Pa) |
| Atomic Mass | amu |
| Speed/ velocity | Meter/ Seconds (m/s) |
| Displacement | Meter |
| Acceleration | Meter/second2 (m/s2 ) |
| Force | Newton Kg ms-2 |
| Momentum | Kg ms-1 |
| Work | Joule (Nm) |
| Energy/PE/KE | Joule (Nm) |
| Power | Watt (w or j/s-1) |
Periodic Table Elements
| Atomic No. | Name of elements | Atomic Weight | Electron Conflagration |
| 1. | Hydrogen (H) | 1 | 1s1 |
| 2. | Helium (He) | 4 | 1s2 |
| 3. | Lithium (Li) | 7 | 1s2,2s1 |
| 4. | Beryllium (Be) | 9 | 1s2, 2s2 |
| 5. | Boron (B) | 10 | 1s2, 2s2 2p1 |
| 6. | Carbon | 12 | 1s2 ,2s2 2p2 |
| 7. | Nitrogen | 14 | 1s2 , 2s2 2p3 |
| 8. | Oxygen | 16 | 1s2 ,2s2 2p4 |
| 9. | Fluorine | 19 | 1s2 ,2s2 2p5 |
| 10. | Neon | 20 | 1s2 , 2s2 2p6 |
| 11. | Sodium | 23 | 1s2 , 2s2 2p6,3s1 |
| 12. | Magnesium | 24 | 1s2 , 2s2 2p6, 3s2 |
| 13. | Aluminum | 26 | 1s2 , 2s2 2p6, 3s2 3p1 |
| 14. | Silicon | 28 | 1s2 , 2s2 2p6,3s2 3p2 |
| 15. | Phosphorus | 30 | 1s2 , 2s2 2p6,3s2 3p3 |
| 16. | Sulfur | 32 | 1s2 , 2s2 2p6, 3s2 3p4 |
| 17. | Chlorine | 35.4 | 1s2 , 2s2 2p6,3s2 3p5 |
| 18. | Argon | 39.9 | 1s2 , 2s2 2p6, 3s2 3p6 |
| 19. | Potassium | 39 | 1s2 , 2s2 2p6, 3s2 3p6 ,4s1 |
| 20. | Calcium | 40 | 1s2 , 2s2 2p6, 3s2 3p6 , 4s2 |
| 24 | Chromium | 52 | 1s2 , 2s2 2p6, 3s2 3p6 3d5 , 4s1 |
| 26 | Iron | 55.8 | 1s2 , 2s2 2p6, 3s2 3p63d6 ,4s2 |
| 29 | Copper | 63.5 | 1s2 , 2s2 2p6, 3s2 3p63d10 , 4s1 |
| 30 | Zinc | 65.3 | 1s2 , 2s2 2p6, 3s2 3p63d10 ,4s2 |
- Average Speed If an object travels with constant speed, then the formula for the speed of the object is given by
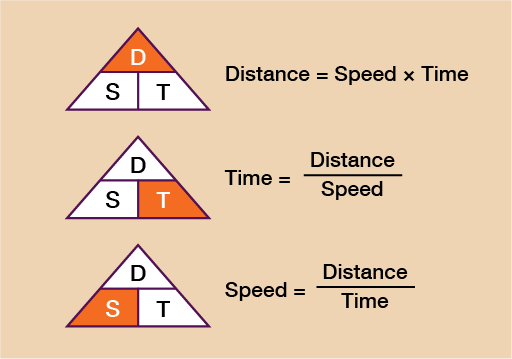
The fundamental Formula is:


Important Definition
| Terms | Formula |
| Pressure | P=F/A, F is a force applied to an area, A, that is perpendicular to the force 1 Pa=1 N/m2 |
| Work | W = Fl W = work (Nm, J),F = applied force (N) l = length or distance moved (m) |
| Temperature | Fahrenheit to Celsius- ° C = 5/9 (° F – 32) Celsius to Kelvin- K = ° C + 273 |
| Power | P = F × v F= Force,(N), V=velocity (m/s) Unit= joule/second. P= W/t W= work (J), t= Time (Seconds) 1 horsepower (hp) = 746 W |
| Work | W = Force * Distance P = Fv cosθ 1 J = 1 N·m |
| Energy | Potential energy (E)= mgh Kinetic energy(E)= 1/2 mv2 ME = mgh + 1/2 mv2 M = mass (Kg), V= velocity (m/s) |
| Torque | τ = r x F The unit of torque ;Newton–meter (N-m) F= Force, r= Distance |
| Momentum |  m=mass and v=velocity Unit- kg•m/s. |
| Acceleration | a=Δv/Δt Δv=change in velocity and Δt=the change in time. Unit= (m s−2) |
| Velocity | velocity = distance / time Unit= m/s |
| force | F = m ⨉ a Unit- kg·m/s2 M= mass, a =Acceleration |
| Density | ρ=m/V Where, ρ=Density, m=Mass of the body, V=The volume of the body |
| Ohms Law Formula: | V= I × R Where, V=Voltage measured in Volts I=Electric current flowing through the conductor in amperes. R=The resistance of the material in ohms. |
| Frequency Formula: | f= V/λ f=Frequency of the wave, V=Velocity or wave speed ,λ=The wavelength of the wave |

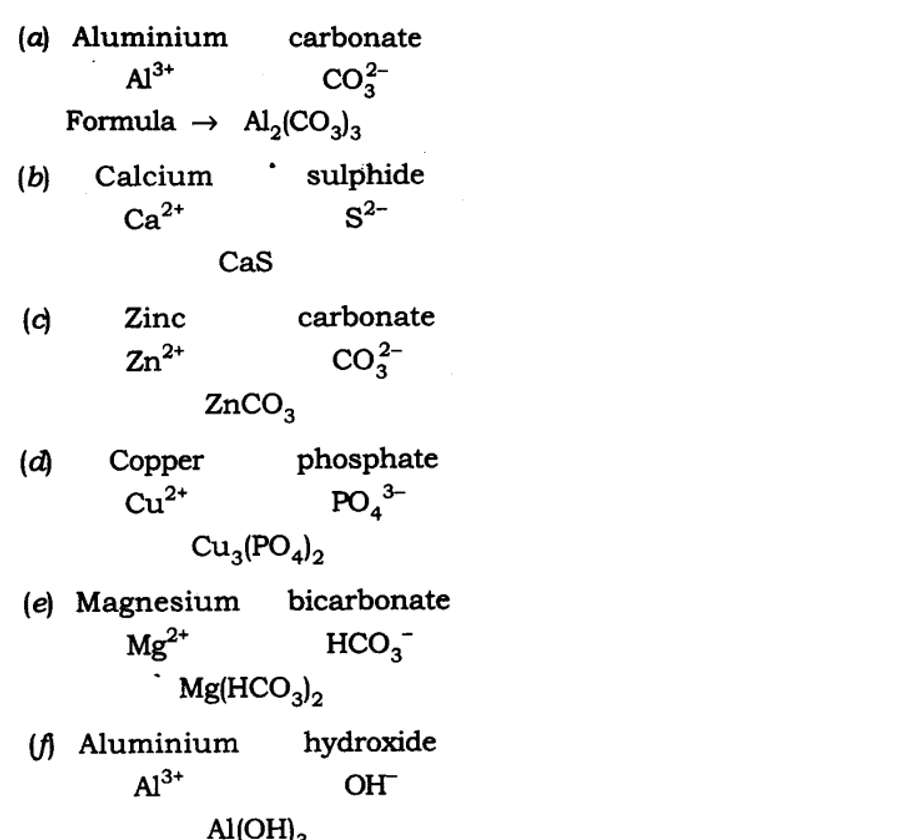

| Symbol Positive Ions | Formula | Symbol Negative Ions | Formula |
| Aluminum | Al. +3 | Bromide | Br– |
| Barium | Ba. +2 | Chloride | Cl– |
| Bismuth | Bi. +3 | Nitride | N3- |
| Cadmium | Cd. +2 | Oxide | O2- |
| Calcium | Ca. +2 | Sulfide | S2- |
| Cesium | Cs. + | Fluoride | F– |
| Chromium (III) | Cr. +3 | Acetate – CH3COO– or C2H3O2- | Sulfate – SO42- |
| Cobalt | Co. +2 | Borate – BO33 | Sulfate – SO42- |
| Copper (I) | Cu+ | Carbonate – CO32- | Thiocyanate – SCN– |
| Copper (II) | Cu+2 | Chlorate – ClO3– Chlorite – ClO2– | Ammonium – NH+4 |
| Hydrogen | H+ | Chromate – CrO42- | Hydronium – H3O+ |
| Iron (II) | Fe+2 | Cyanide CN– | Acetate – CH3COO– or C2H3O2- |
| Iron (III) | Fe+3 | Dichromate – Cr2O72- | Silicate – SiO32- |
| Zinc | Zn+2 | Hydrogen sulfate – HSO4– | |
| Silver | Ag+ | Hydrogen phosphate – HPO42- | |
| Sodium | Na+ | Hydroxide OH– | |
| Potassium | K+ | Nitrate – NO3– | |
| Nickel | Ni+2 | Nitrite – NO2– | |
| Lithium | Li+ | Oxalate – C2O42- | |
| Magnesium | Mg+2 | Phosphate – PO43 | |
| Lead (II) | Pb+2 | Phosphite – PO33- |
Mathematics Formula
Mathematics Class-5 to 8 Formula Notes is always based on different conspectus formulas subtraction,Addition, multiplication, Division, percentage,real No. ,prime no. , Average, Mean,Triangle,square, Right Triangle,area,volume perimeter etc.basic fundamental idea is important for increasing the speed in mathematics subject few important formula in class 5 to 8 student for build the basic put the foundation with help of this conspectus.Click here
Quiz also here and Mathematics cheater Science & Mathematics Quiz
Fundamental Formula Details
| Addition | |
| Subtraction | |
| Multiplication | |
| Division |  |
| Basic Division Conspectus | 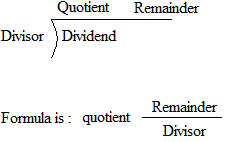 |
| Proportion: |  |
| Percent | x% = x/100 |
| Decimal to Percentage | .x=.x×100=x% |
Area, Volume, Perimeter Details
| Sr.No | Geometry of Body | Area | Perimeter |
| 1. | Rectangle | A=LW the rectangle’s sides (length and width). | P=(2L+2W) L and W W are the lengths of the rectangle’s sides (length and width). |
| 2. | Square | A=s2 s is the length of the side of the square. | P=4s s is the length of the side of the square. |
| 3. | Triangle | A=1/2(b*h) b and h h are the base and height | a+b+c a.b , and c c are the side lengths. |
| 4. | Circle | A=πr2 r is the radius. | P=2πr=πd r is the radius and d d is the diameter. |
| 5. | Parallelogram | A=b*h b is the length of the base and h h is the height. | P=2(a+b) b=Base, a=Side |
| 6. | Trapezoid | A=(b1 + b2)/2 *h b1 and b2 are the lengths of the parallel sides and h h the distance (height) between the parallels. | 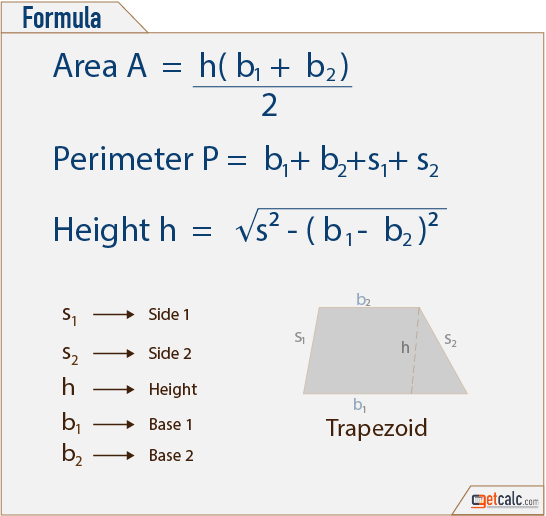 |
| 7. | Equilateral triangle | – |  |
| 8. | Isosceles Triangle | 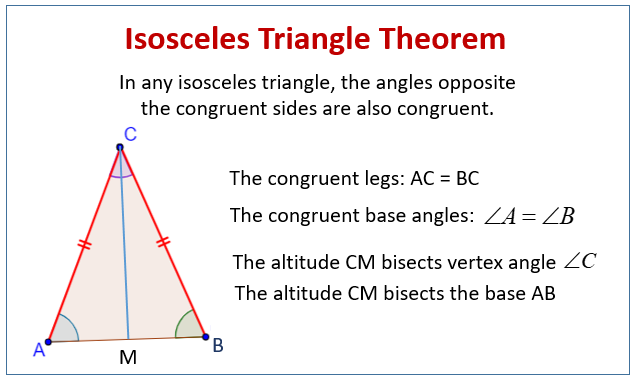 |  |
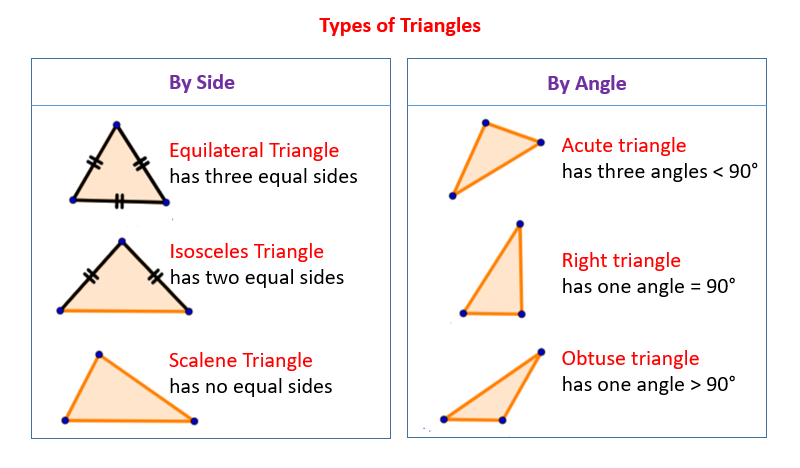
Volume Formula on Geometry
| Geometry | Volume body | Image of substance |
| Volume of A Cube | Volume of the cube = s3 s is the length of one of its sides | 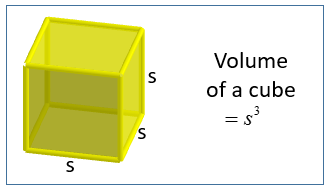 |
| Volume Of A Rectangular Solid | l × w × h where l is the length, w is the width and h is the height | 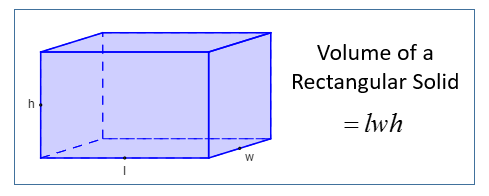 |
| Volume Of A Prism | V = Al where A is the area of the base and l is the length or height of the prism | 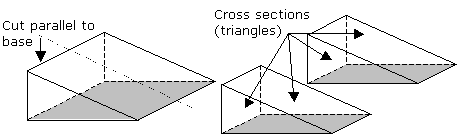 |
| Volume Of A Cylinder | V = π r2h where r = radius of cylinder and h is the height or length of cylinder. | 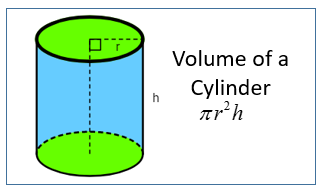 |
| Volume Of A Hollow Cylinder | where _R_ is the radius of the outer surface and _r_ is the radius of the inner surface | 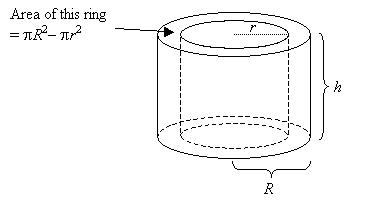 |
| Volume Of A Cone | V = 1/3 πr2h where r is the radius of the base and h is the height of the prism. | 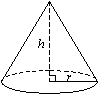 |
| Volume of a Pyramid | V = 1/3 A*h where A is the area of the base and h is the height of the pyramid. | 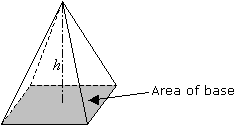 |
| Volume of a Sphere | 4/3 πr3 where r is the radius. | 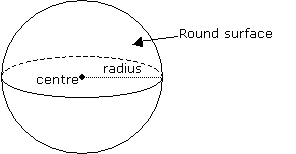 |
| Volume of a hemisphere | 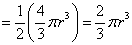 where r is the radius. | 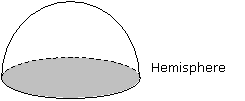 |
